The Impact of Sexual Dysfunction
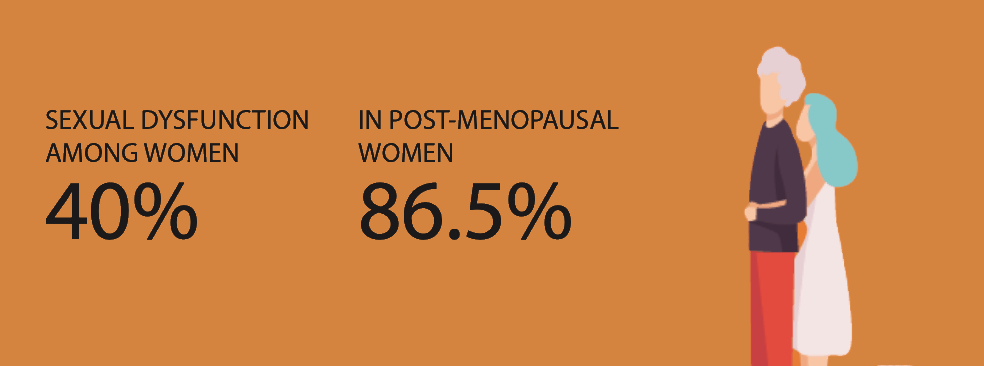
Sexual dysfunction, which I see commonly in my women’s health practice, is distressing for relationships, quality of life, and confidence. The prevalence of this issue among women is estimated to be 40%, and in postmenopausal women, 86.5%. There are three phases of decline: 1) desire, 2) arousal, and 3) climax.
Desire relates to an interest in sex while arousal relates to blood flow. Common medical conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and urinary incontinence are known to affect sexual function. Prescription drugs for cholesterol, blood pressure, depression, and contraception can impact sexual function as do non-prescription medications such as antihistamines, antifungals, and anti-inflammatories. Oral birth control pills increase certain proteins which reduce free testosterone and can lower sex drive, however, estrogen birth control delivered in a patch (transdermal instead of oral) has been shown not to affect sexual function.
Also, psychological factors such as body image, emotional neglect, relationship discord, retirement, children leaving home, and depression can affect sexual function. Counselling can be beneficial to mitigate the impact. Moreover, mindfulness-based interventions have been shown to treat low sexual desire, arousal, and climax effectively. By far, ageing has the largest impact on sexual function with declining hormones, especially estrogen and testosterone. During menopause, the gradual shutting down of ovarian hormones leads to a genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM) – vaginal dryness, burning, irritation, urinary urgency, painful urination, and recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs). As part of the ageing process, GSM can lead to dysfunctional pelvic floor muscles, and in this instance, pelvic floor physical therapy can be helpful.
Solutions for Low Libido
Osphena ®
A new FDA-approved option is a non-estrogen medication that reverses certain changes in vaginal tissue caused by menopause, thus improving the pH as well as relieving symptoms of dryness.
Estrogen
A treatment for GSM offers help for libido. Topical vaginal estrogen cream (transdermal) is preferred over oral systemic estrogen. Long-term use of topical vaginal estrogen cream has been given the nod of approval by the American College of Oncologists. This is good news! In my practice, bio-identical estriol cream has helped women overcome GSM and enjoy intimacy again.
Testosterone
Data on the benefits of testosterone therapy are limited and inconsistent. Androgens are positively associated with improvements in all aspects of sexual functioning (desire, arousal, vaginal blood flow, and climax), but testosterone blood levels have not been connected to female sexual function. Randomized controlled trials involving menopausal women with low sexual desire or arousal have shown improvements in sexual function with short-term transdermal testosterone therapy. However, data on long-term risks and benefits are lacking. Plus, the Endocrine Society does not recommend long-term testosterone treatment. Testosterone therapy is not FDA approved for use in women, and the formulations made for men are discouraged. Testosterone supplementation is a popular trend, but women should be cautious, under a doctor’s supervision, and also watch out for side effects. Delayed or less-intense climax is believed to be a natural process of ageing-related to decreased genital blood flow and dulled sensations. Prescription medication to increase genital blood flow, such as Viagra, has been studied in women without success.
Sex Essentials ®
It is a non-prescription natural dietary supplement for libido that has helped my patients. How does it help? As women approach their 50s (perimenopause), climax can take much longer as blood flow and sensation change. Sex Essentials has helped my patients feel more desire, shorten time for arousal, and intensify height and duration of climax. Sex Essentials contains L-arginine, gingko biloba, and Korean ginseng, and can help improve blood flow to sexual organs as well as enhance physical capacity and performance.
L-arginine
A precursor of nitric oxide in the human body. Higher levels of nitric oxide result in increased blood flow, which makes the penile, clitoral, and vaginal tissues more sensitive and responsive to sexual stimulation. A study involving 77 women of all ages found that after four weeks, 73.5% of the women who took a supplement including L-arginine experienced greater sexual satisfaction, plus heightened desire and clitoral sensation, frequency of intercourse and orgasm, and less vaginal dryness.
Gingko biloba
A well known for its ability to promote blood circulation and oxygen flow throughout the body which improves sensitivity and sexual response.
Korean ginseng
It has been shown to help enhance sexual function in both men and women. A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind crossover trial found that supplementation with ginseng in menopausal women increased sexual arousal, satisfaction, and frequency. Studies have also shown clear benefits in men with reported improvements in libido, erectile function, and testosterone levels.
In all my years of clinical practice, I’ve come to realize that many components for a loving relationship, don’t necessarily come in a bottle, but from care, trust, and commitment, to name a few. It is also comforting to know that medical science and natural products can assist the body as it ages, to keep a relationship loving, joyful, and content.
The Impact of Sexual Dysfunction
Sexual dysfunction, which I see commonly in my women’s health practice, is distressing for relationships, quality of life, and confidence. The prevalence of this issue among women is estimated to be 40%, and in postmenopausal women, 86.5%. There are three phases of decline: 1) desire, 2) arousal, and 3) climax. Desire relates to an interest in sex while arousal relates to blood flow.
Common medical conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and urinary incontinence are known to affect sexual function. Prescription drugs for cholesterol, blood pressure, depression, and contraception can impact sexual function as do non-prescription medications such as antihistamines, antifungals, and anti-inflammatories. Oral birth control pills increase certain proteins which reduce free testosterone and can lower sex drive, however, estrogen birth control delivered in a patch (transdermal instead of oral) has been shown not to affect sexual function.

Also, psychological factors such as body image, emotional neglect, relationship discord, retirement, children leaving home, and depression can affect sexual function. Counselling can be beneficial to mitigate the impact. Moreover, mindfulness-based interventions have been shown to treat low sexual desire, arousal, and climax effectively. By far, ageing has the largest impact on sexual function with declining hormones, especially estrogen and testosterone. During menopause, the gradual shutting down of ovarian hormones leads to a genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM) – vaginal dryness, burning, irritation, urinary urgency, painful urination, and recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs). As part of the ageing process, GSM can lead to dysfunctional pelvic floor muscles, and in this instance, pelvic floor physical therapy can be helpful.

Solutions for Low Libido
Osphena®
A new FDA-approved option is a non-estrogen medication that reverses certain changes in vaginal tissue caused by menopause, thus improving the pH as well as relieving symptoms of dryness.
Estrogen
A treatment for GSM offers help for libido. Topical vaginal estrogen cream (transdermal) is preferred over oral systemic estrogen. Long-term use of topical vaginal estrogen cream has been given the nod of approval by the American College of Oncologists. This is good news! In my practice, bio-identical estriol cream has helped women overcome GSM and enjoy intimacy again.
Testosterone
Data on the benefits of testosterone therapy are limited and inconsistent. Androgens are positively associated with improvements in all aspects of sexual functioning (desire, arousal, vaginal blood flow, and climax), but testosterone blood levels have not been connected to female sexual function. Randomized controlled trials involving menopausal women with low sexual desire or arousal have shown improvements in sexual function with short-term transdermal testosterone therapy. However, data on long-term risks and benefits are lacking. Plus, the Endocrine Society does not recommend long-term testosterone treatment. Testosterone therapy is not FDA approved for use in women, and the formulations made for men are discouraged. Testosterone supplementation is a popular trend, but women should be cautious, under a doctor’s supervision, and also watch out for side effects. Delayed or less-intense climax is believed to be a natural process of ageing-related to decreased genital blood flow and dulled sensations. Prescription medication to increase genital blood flow, such as Viagra, has been studied in women without success.
Sex Essentials®
It is a non-prescription natural dietary supplement for libido that has helped my patients. How does it help? As women approach their 50s (perimenopause), climax can take much longer as blood flow and sensation change. Sex Essentials has helped my patients feel more desire, shorten time for arousal, and intensify height and duration of climax. Sex Essentials contains L-arginine, gingko biloba, and Korean ginseng, and can help improve blood flow to sexual organs as well as enhance physical capacity and performance.
L-arginine
A precursor of nitric oxide in the human body. Higher levels of nitric oxide result in increased blood flow, which makes the penile, clitoral, and vaginal tissues more sensitive and responsive to sexual stimulation. A study involving 77 women of all ages found that after four weeks, 73.5% of the women who took a supplement including L-arginine experienced greater sexual satisfaction, plus heightened desire and clitoral sensation, frequency of intercourse and orgasm, and less vaginal dryness.
Gingko biloba
A well known for its ability to promote blood circulation and oxygen flow throughout the body which improves sensitivity and sexual response.
Korean ginseng
It has been shown to help enhance sexual function in both men and women. A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind crossover trial found that supplementation with ginseng in menopausal women increased sexual arousal, satisfaction, and frequency. Studies have also shown clear benefits in men with reported improvements in libido, erectile function, and testosterone levels.
In all my years of clinical practice, I’ve come to realize that many components for a loving relationship, don’t necessarily come in a bottle, but from care, trust, and commitment, to name a few. It is also comforting to know that medical science and natural products can assist the body as it ages, to keep a relationship loving, joyful, and content.
References
- Shifren JL, Mons BU, Russo PA, et al. Sexual problems and distress in United States women: prevalence and correlates. Obstet Gynecol. 2008; 112(5):970-978.
- Buster JE. Managing female sexual dysfunction. Fertil Steril. 2013; 100(4):905-915.
- Kingsberg SA, Rezaee RL. Hypoactive sexual desire in women. Menopause. 2013; 20(12):1284-1300.
- Rosenbaum TY. Musculoskeletal pain and sexual function in women. J Sex Med. 2010; 7(2pt 1):645-653.
- Davis SR, Van der Mooren MJ, Van Lunsen RH, et al. Efficacy and safety of a testosterone patch
for the treatment of hypoactive sexual desire disorder in surgically menopausal women: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Menopause. 2006; 13(3):387-396.














